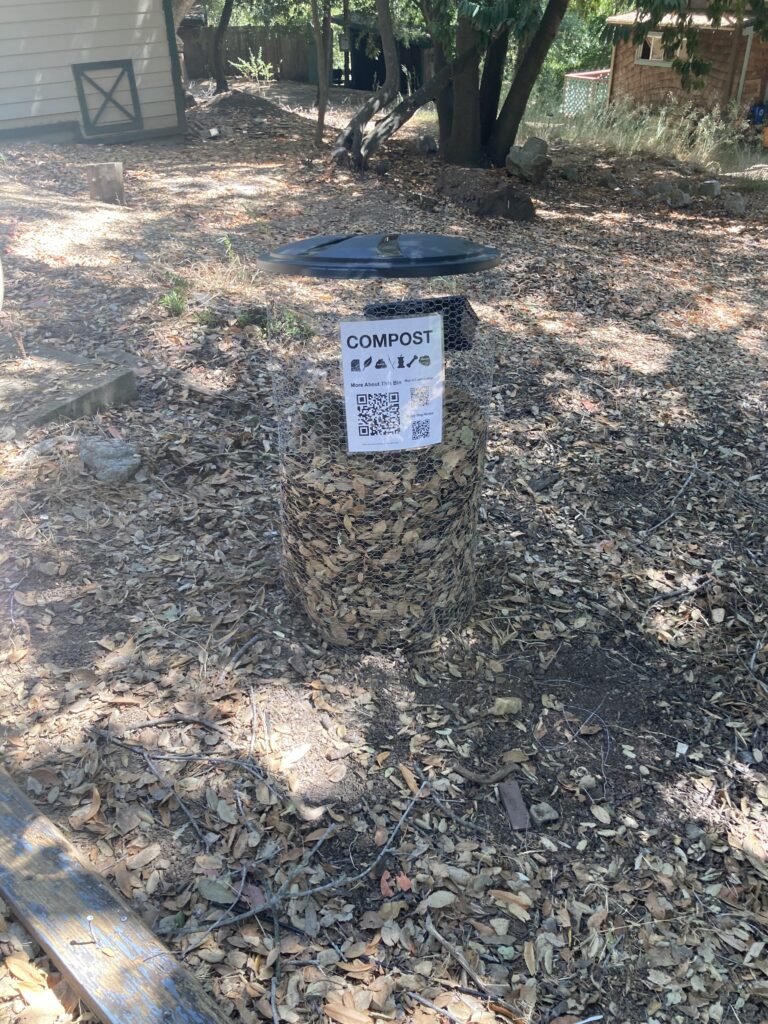
Grow local resources by depositing compost and sharing seeds at the Greencycle Bin!
Grow local resources by depositing compost and sharing seeds at the Greencycle Bin!
Compost enriches soil for nearby plants and increases soil moisture.
Share seeds in the attached seed bank.
Compost
Add the following components:
- torn paper products
- wood chips, twigs
- leaves
- fruit
- animal remains (such as/ eggs, feathers, bones, nail clippings, etc)
- animal manure (domesticated or wild)
- wastewater (only biodegradable soaps)
- food waste
- charcoal
- ash
When adding food waste, animal remains, or manure, make sure to cover with wood chips, twigs, leaves, charcoal, or soil.
Compost questions
What kind of food waste can be added?
Common compost advice is to avoid adding cooked food, oil, dairy, or meat to compost, due to their potential to attract pests. However, when covered with other biomass they break down quickly and become part of healthy soil.
Learn about composting food waste
Why animal remains?
Bodies are a great source of nitrogen and other nutrients for feeding plants.
Learn about composting animal waste
Fact: Indigenous Amazonians included carcasses, food waste. manure, tree debris, ash and charcoal in their engineered soil, “Terra Preta,” which they used to increase the biodiversity of the Amazon rainforest.
Why manure?
Manure is nutrient rich medium for growing plants.
For this compost bin, we recommend adding manure of pets or wildlife.
Learn about how to compost humanure
Both manure and carcasses can be safely composted in these composters, provided contribution of diverse biomass and increased temperature in the presence of charcoal.
Why charcoal?
Charcoal is a porous, conductive form of pure carbon that can retain water and diverse bacterial cultures. Soil fungus uses charcoal as a medium to network bacterial byproducts to plants, increasing plants’ growth, health, and yield. Due to charcoal’s moisture retention, charcoal confers drought resistance to the plants and soil.
When charcoal added to compost, it is called “biochar.”
Biochar has been used by indigenous Amazonians and modern researchers to increase biodiversity that the soil can support, as well as remediate soil of heavy metals, antibiotics, herbicides, pesticides and other chemical excesses.
Biochar increases rate of decomposition and temperature of compost (from an average of 120°F to 130°F).
Biochar is recommended for consisting of up to 10% of the compost mass.
Why ash?
In small quantities, ash is a helpful soil amendment that contains calcium, carbon and potassium.
In excess, ash can lower the pH of soil.
Seed Bank
- Deposit seeds in theirvessels
- Label the vessel with the kind of plant. Include the breed/variety, location & season harvested, if known.
- Select seeds appropriate for the location you would like to sow at (as described on the package or internet source)
Seed bank questions
When do I sow?
Typically sowing instructions are to plant the seed under 1/2” of soil in Fall or Spring, depending on its growing patterns. However, seasons in California have been fluctuating and annual crops have thrived throughout the year.
If the plant needs a substantial amount of water to germinate, you can sow during the rainy season or start the seed in a planter.*
*In light of the water crisis, we recommend watering container plants with waste water collected from dishes, if using a light biodegradable soap (Dawn or Dr. Bronners)
Can I grow [plant type] here?
We are in zone 10, appropriate for many temperate, subtropical, and tropical plants. Historically our winters have had cold snaps that reach below freezing for around a week at a time. In recent years, our winters have been warmer and many cold-sensitive plants have survived living in the ground outdoors.